Jamstack
From the Jamstack website:
Jamstack is an architectural approach that decouples the web experience layer from data and business logic, improving flexibility, scalability, performance, and maintainability.
Jamstack removes the need for business logic to dictate the web experience.
It enables a composable architecture for the web where custom logic and 3rd party services are consumed through APIs.
More details
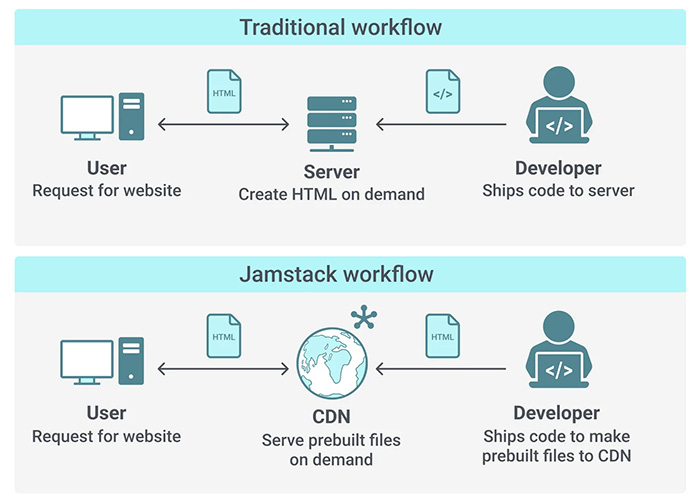
Jamstack stands for JavaScript, APIs, and Markup
It emphasizes building fast, secure, and scalable websites and web applications by pre-rendering static files during the build process and serving them directly to the client via a content delivery network (CDN)
This approach reduces server-side processing:
- Enhanced performance - content is generated at build time, reducing server load
- Easier maintenance and scaling - decoupling separates frontend and backend
- Better security - fewer server-side vulnerabilities due to reduced attack surface
Prebuilt Markups
- In Jamstack architecture, the markup should be prebuilt
- The server doesn’t create the markups on every client request.
- It makes the initial load of the app very fast
Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- CDN reduces the distance between the users and application resources
- CDN reduces the amount of data transfer using minification techniques
- CDN helps in cache invalidation so that users do not see old data
Automated Build and Deployment
- Jamstack application source code must be in a Version Control System, like Git
- The CDN/ App Hosting providers can create integrations with a Git-supported platform like GitHub
- It provides significant flexibility to kick-off a build when there is a new commit tracked in GitHub
- When the build succeeds, the built version gets deployed to preview as well
Practically Serverless
- Jamstack architecture and the Serverless application architecture have a significant overlap
- For example, you may need an authentication system, an emailing system and a form management tool
- You do not need to build them at all, you consume them as services using the APIs provided by the vendors
High level
- Developers write code, commit and push it to a source repository application like GitHub.
- The integration with a CDN provider kicks off a workflow that starts the build to create prebuilt content.
- The prebuilt content then gets deployed to a CDN by the CDN provider, and a unique secured URL gets generated for you. The URL gets generated for every commit so that you can preview the app in a production environment before deploying them.
- You share this URL with your end-users or customers to access the app.
- Users request the resources from the CDN that is serving the prebuilt content.
- For any services, the API call goes to separate microservices hosted on the cloud.
Jamstack Architecture: What, Why, and How?
Static Site Generators - Top Open Source SSGs | Jamstack
Tools that generate static HTML files based on templates and content, simplifying the process of building and deploying static websites.
- Next.js
- Gatsby
- Docosaurus
- Nuxt
- Hexo
- Astro
- 11ty
Pros and cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Performance: Faster loading times and improved user experience. | Dynamic functionality Limitations: Complex dynamic functionalities may require additional workarounds. |
| Scalability: Easier scaling due to the decoupled architecture and static files. | Learning curve: Requires familiarity with modern frontend tools and workflows. |
| Security: Reduced server-side vulnerabilities and attack surface. | Build times: Initial setup and build times can be longer compared to traditional server-side rendering. |
| Developer experience: Simplified development workflows and easier maintenance. | |
| EO-friendly: Pre-rendered content improves search engine optimization. |
